Contribution guidelines
General guidelines
The contribution interface of SKM allows for logged users to add reactions (and their reference) to the PSS database. In order to create an account, please use the Contact us page to apply for an account invitation.
Contributions start at the Contribute page. The contribution workflow is shown in the following image:
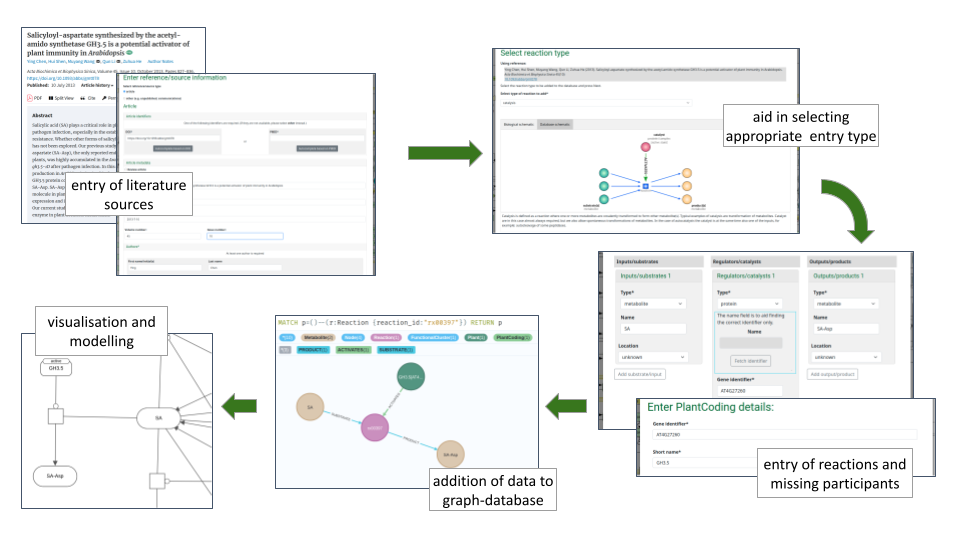
Before you start:
- Note that only direct interactions should be entered.
- The contribution steps will guide you through (1) entering the reference source details, (2) selecting the reaction type, and (3) entering the reaction details.
- Please do not use the browser back or refresh buttons during entry of a reaction.
- foreign nodes refer to external actors, such virus, bacteria, ...
- Please only add one new reaction at a time.
Entering the reference
The first step is to select the type of reference or the source of the new reaction. Two options are available: a research article with a DOI and/or a PubMed identifier, or "other".
When selecting a research article, the DOI or PubMed identifier can be used to autocomplete the information. Apart from this identifier, the required fields are also: article title, a minimum of one author, and the publication date.
When "other" is selected, a short description (<50 characters) and a longer explanation are required.
Selecting the reaction type
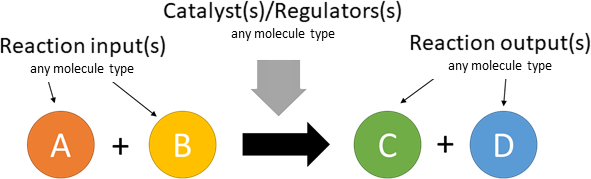
A drop-down menu aids the contributor in selecting the appropriate reaction type. Note that this step is important, as it defines the fields available when entering the reaction details. On selection of a reaction type, a biological representation, database schematic and short description of the selection is shown. These descriptions should be used to confirm sure the reaction that is being entered fits the reaction type.
The following reaction types/definitions are available:
binding/oligomerisation
Biological representation
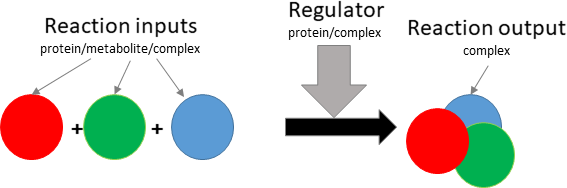
Database representation
dissociation
Biological representation
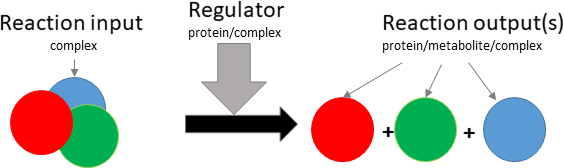
Database representation
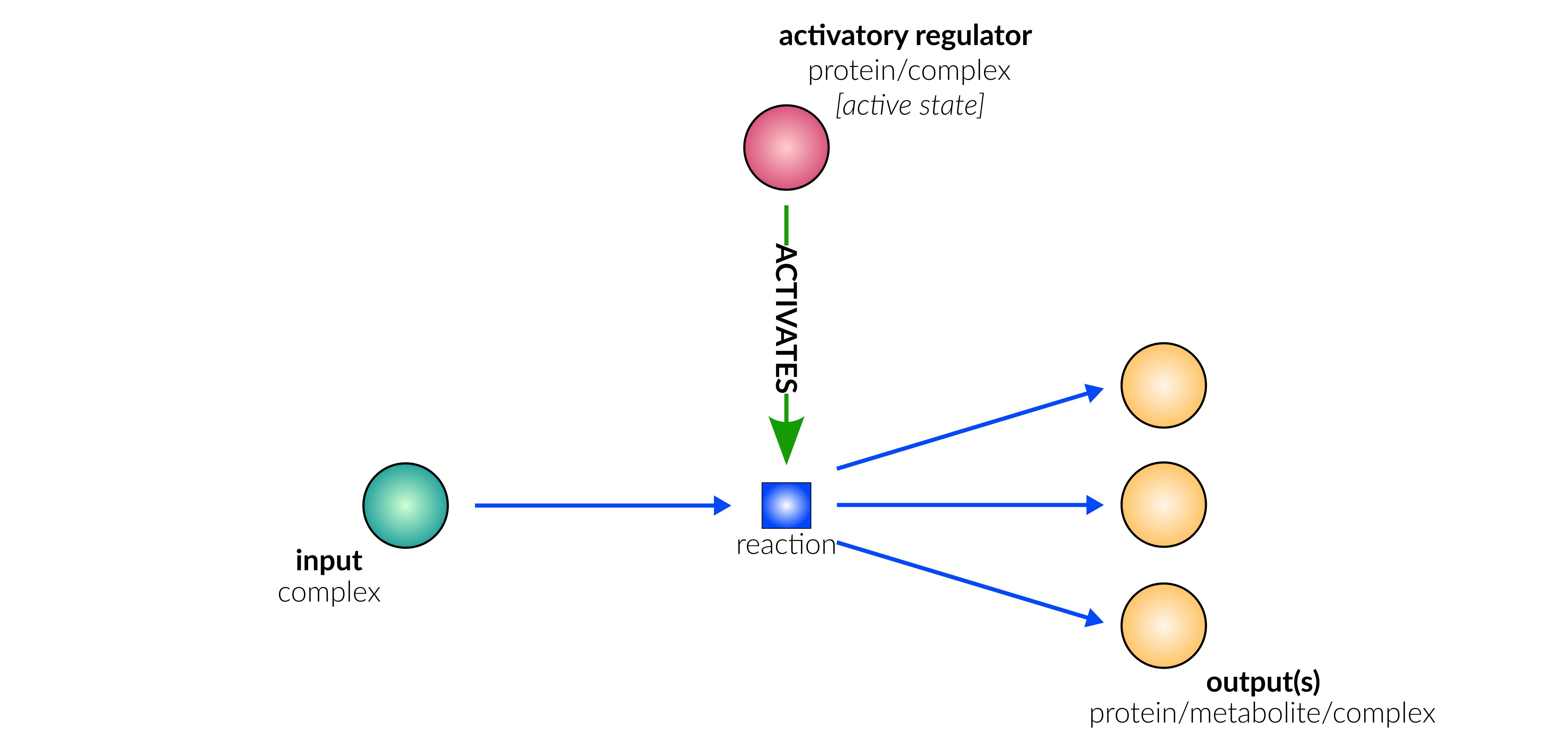
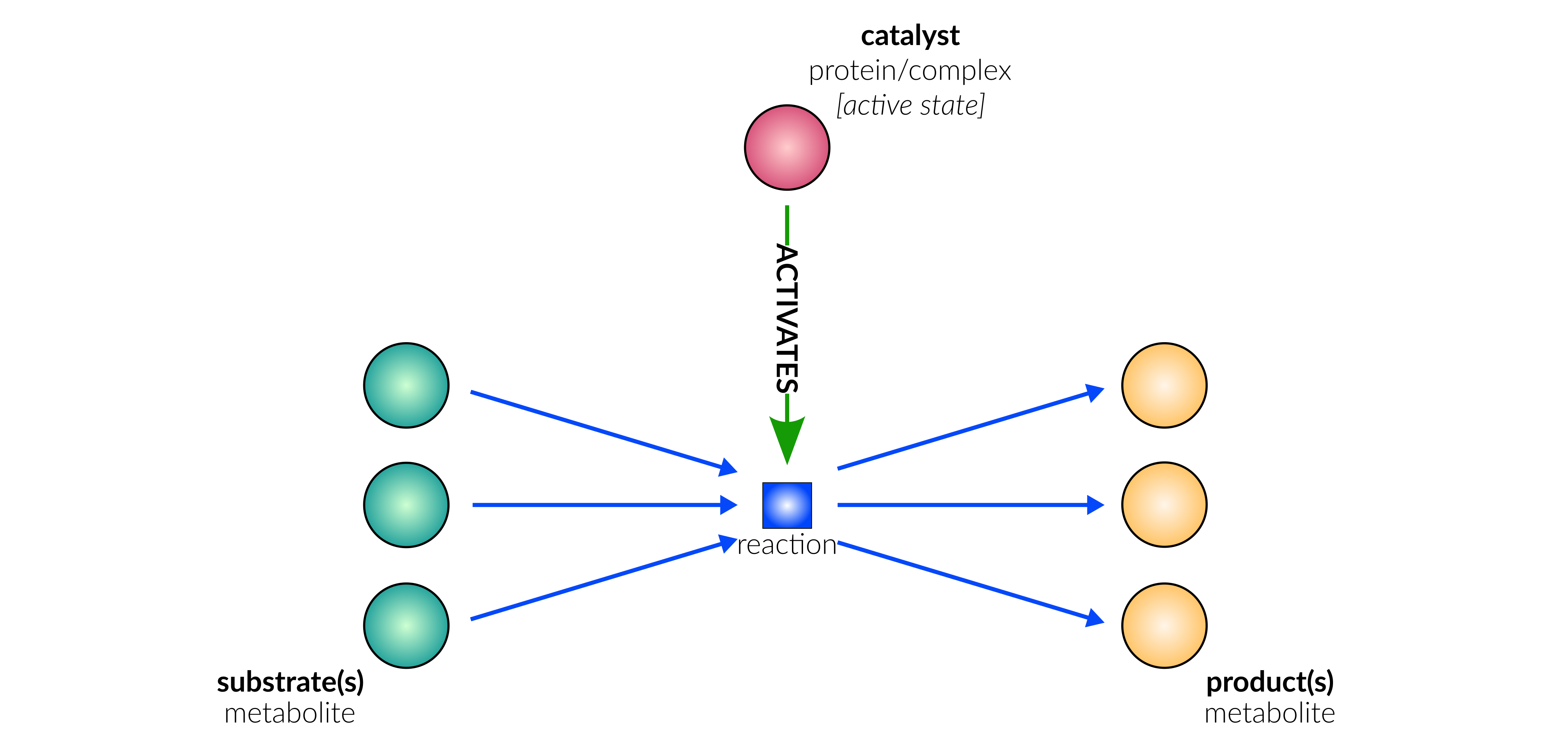
catalysis
Biological representation
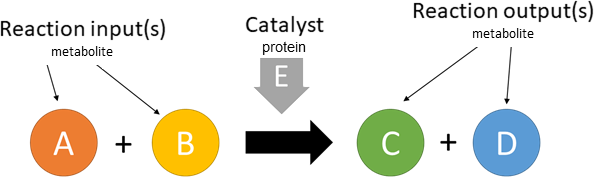
Database representation
degradation/secretion
Biological representation
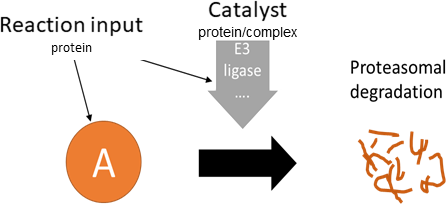
Database representation
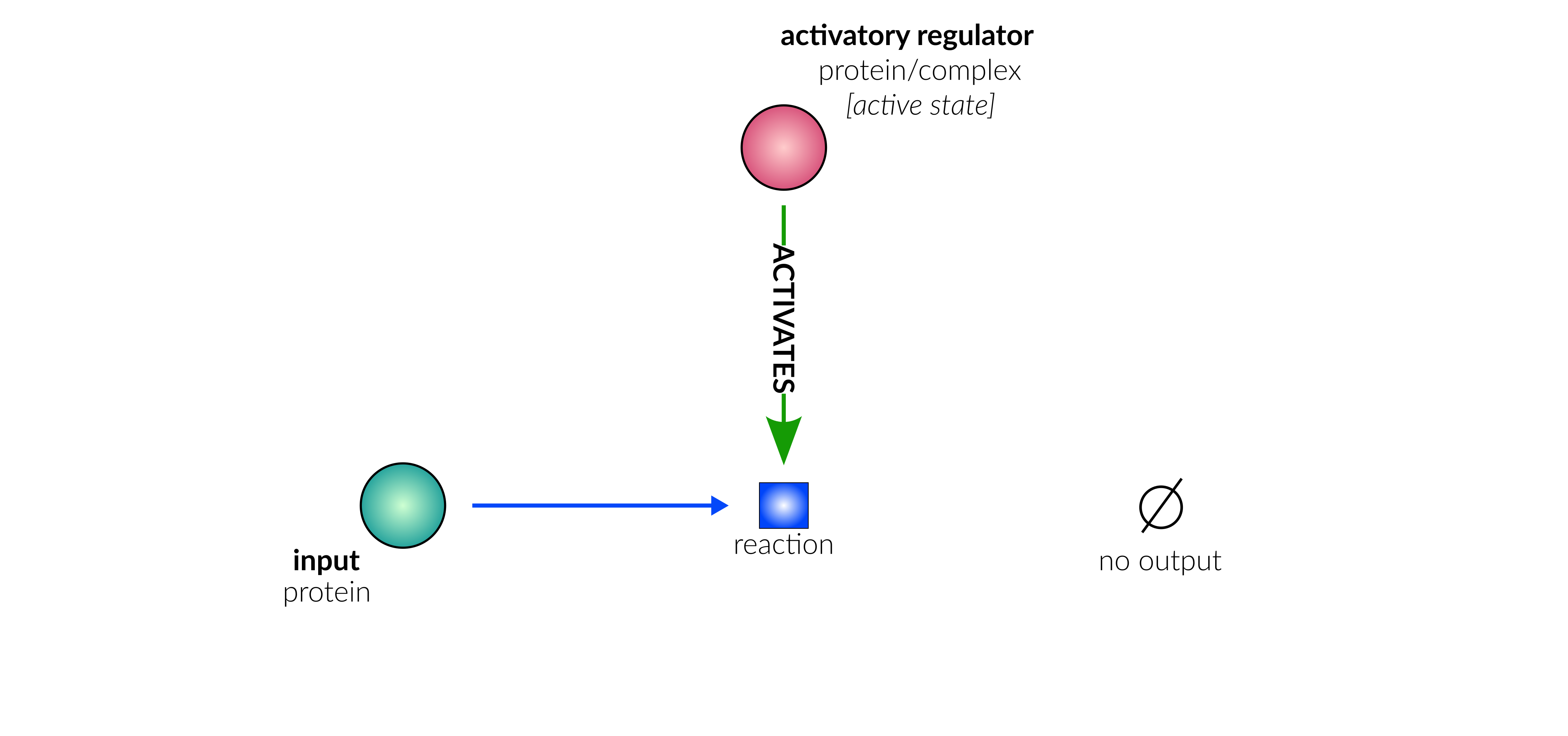
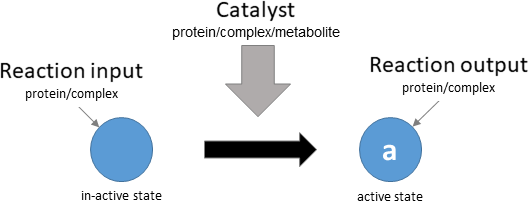
protein deactivation
Biological representation
Database representation
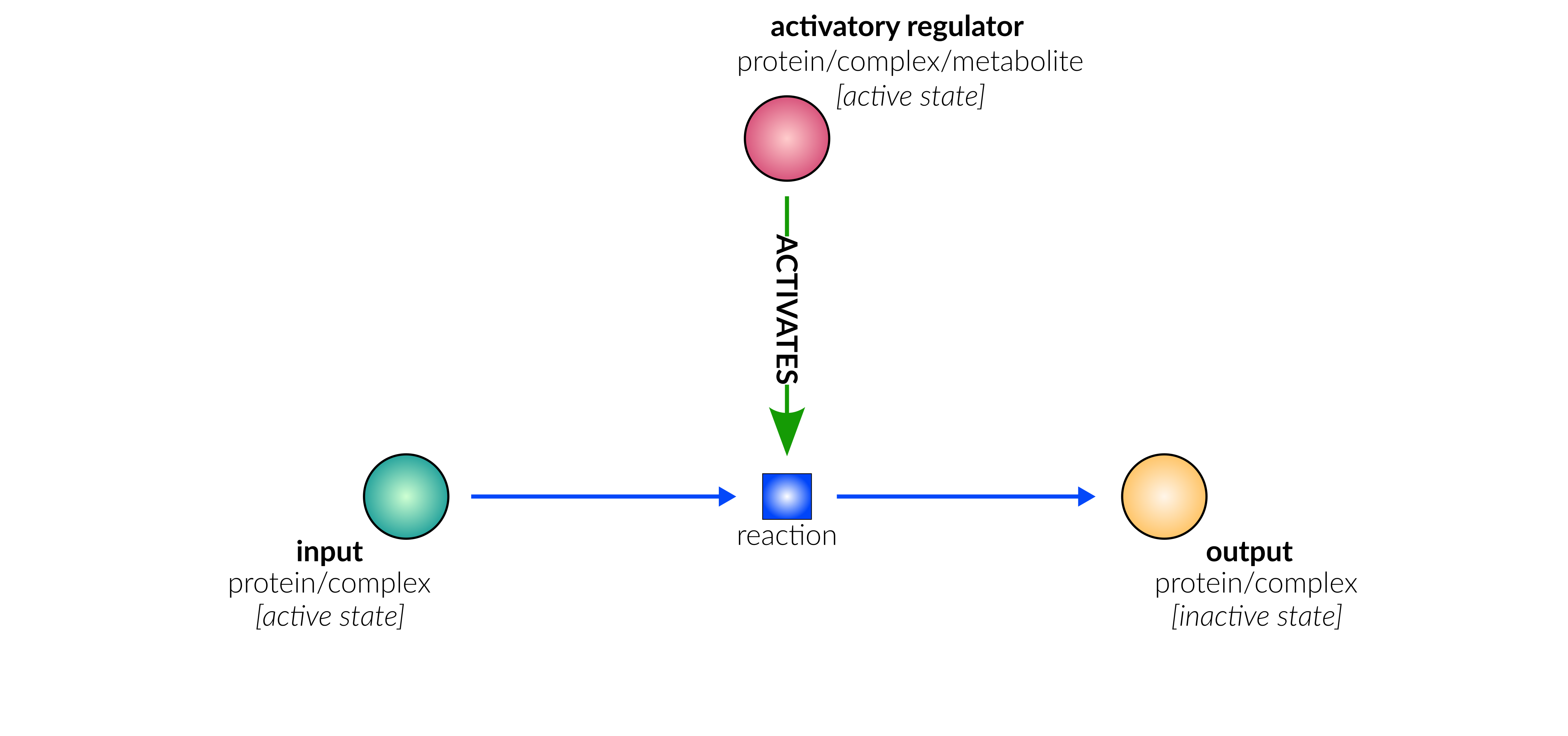
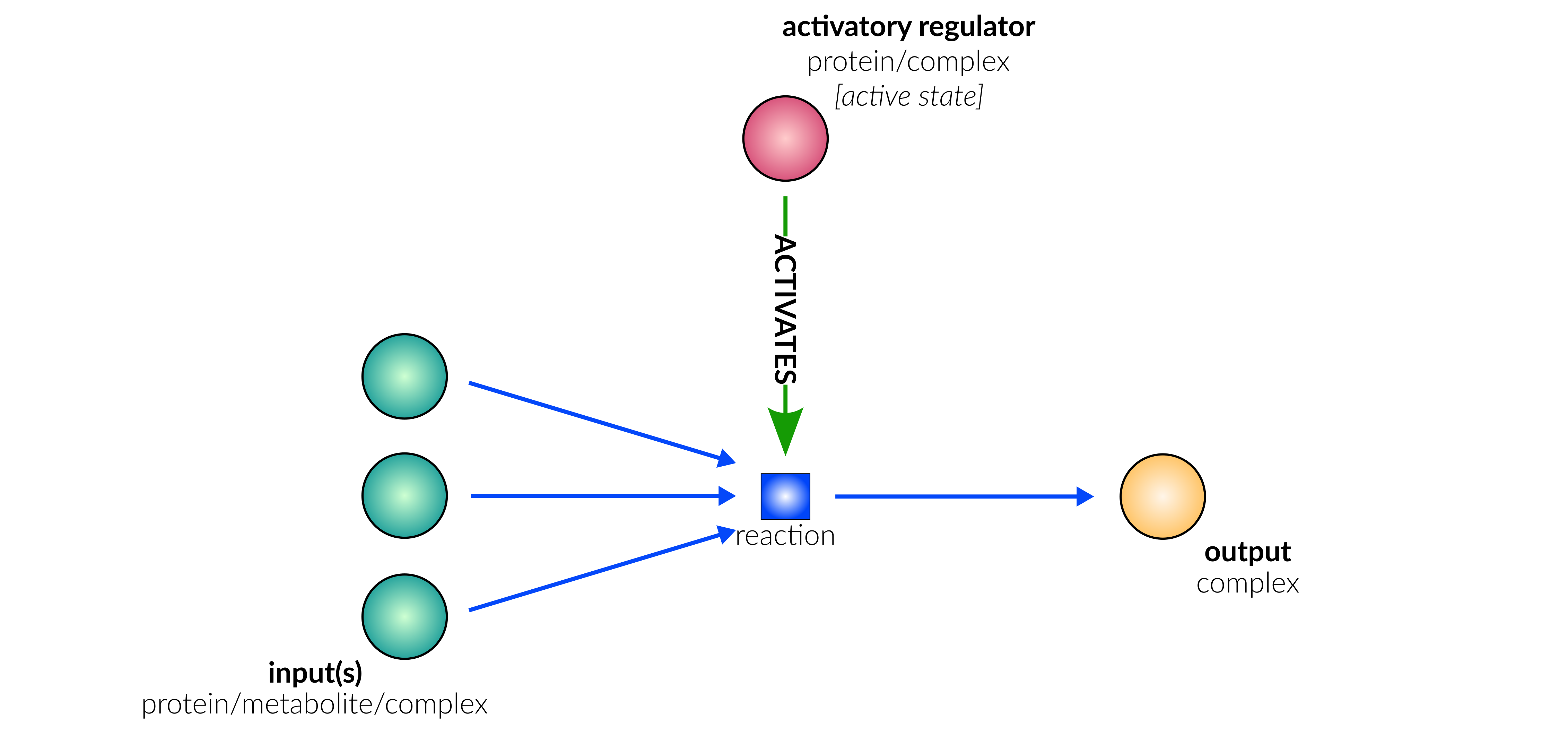
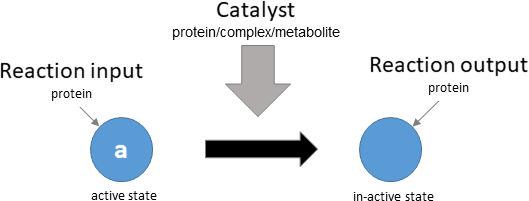
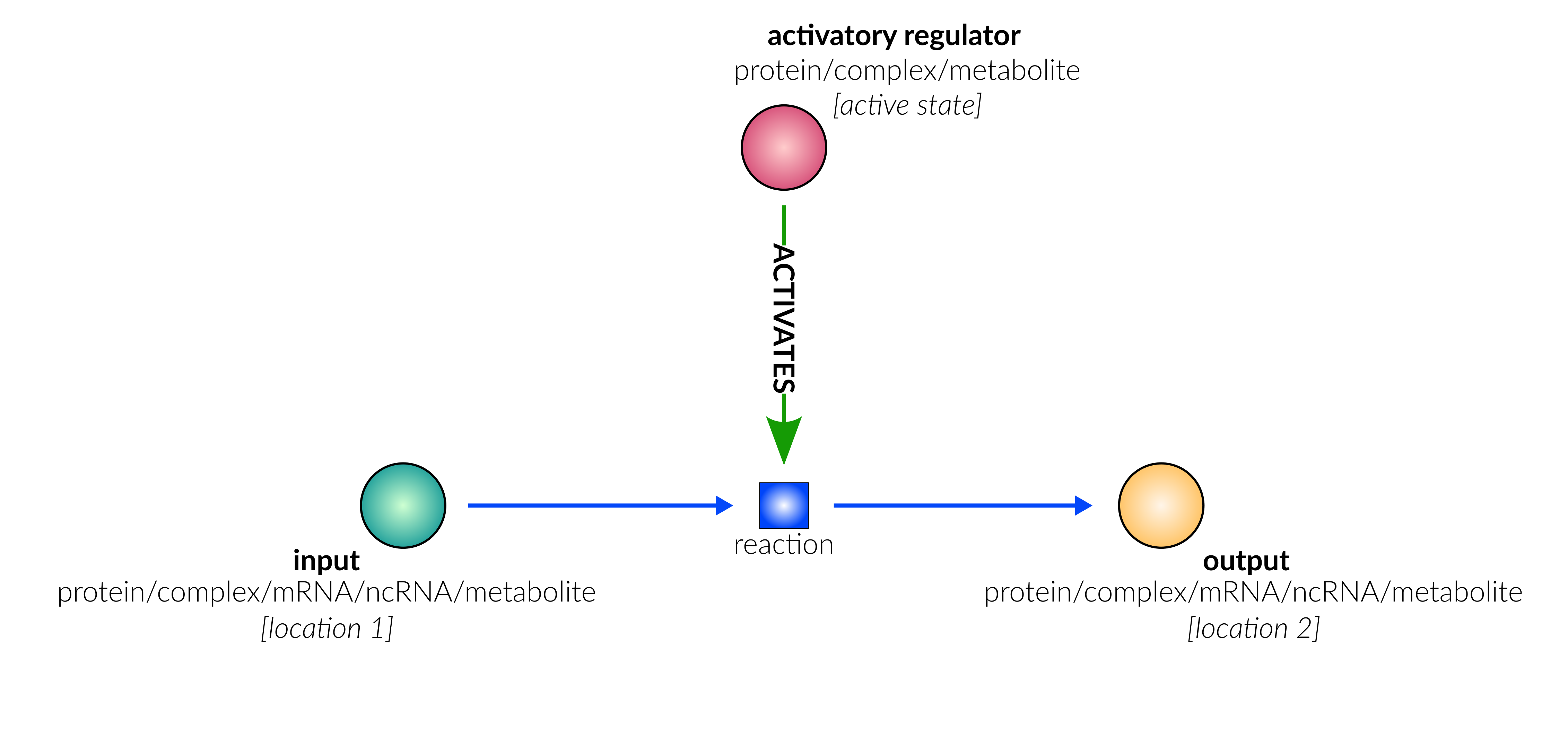
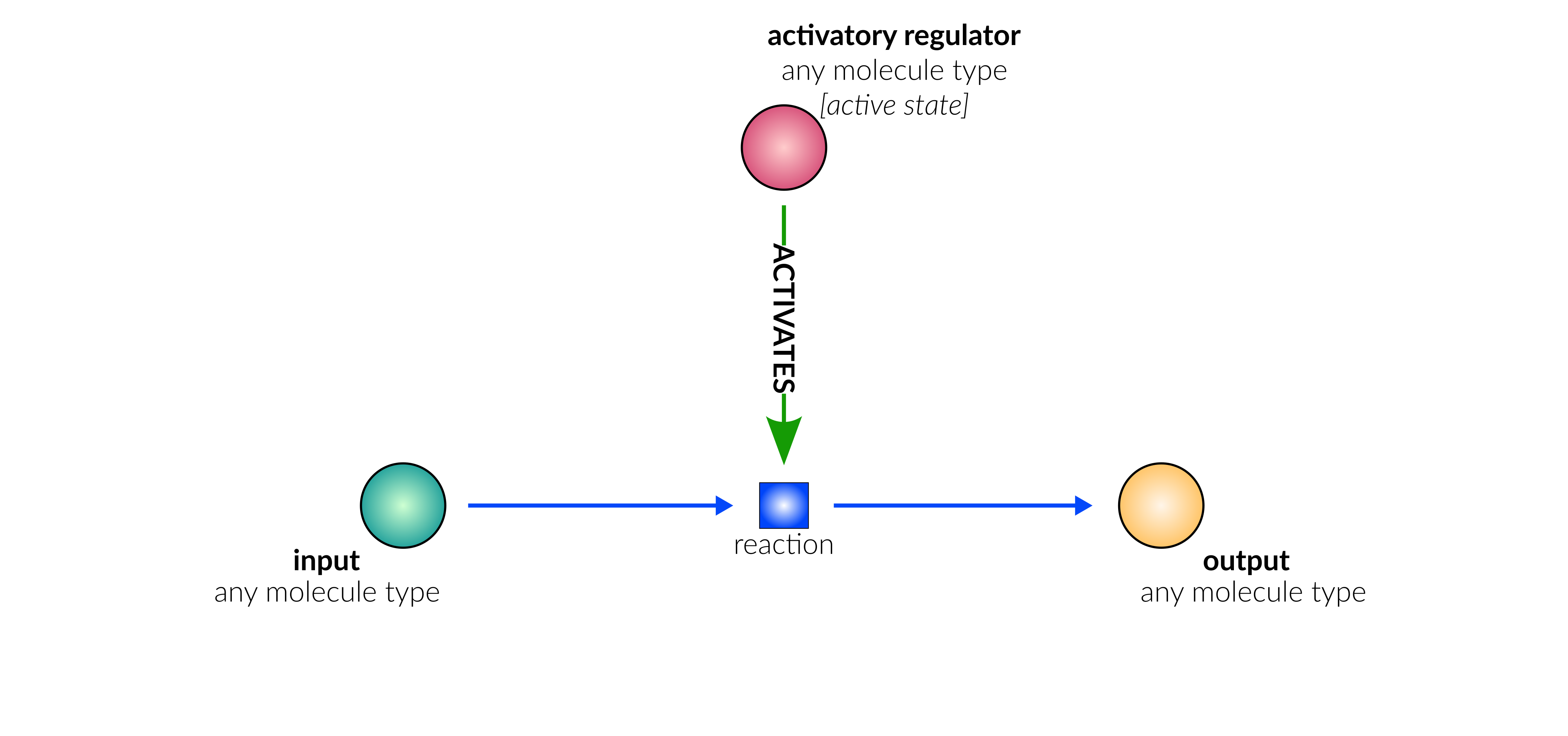
protein activation
Biological representation
Database representation
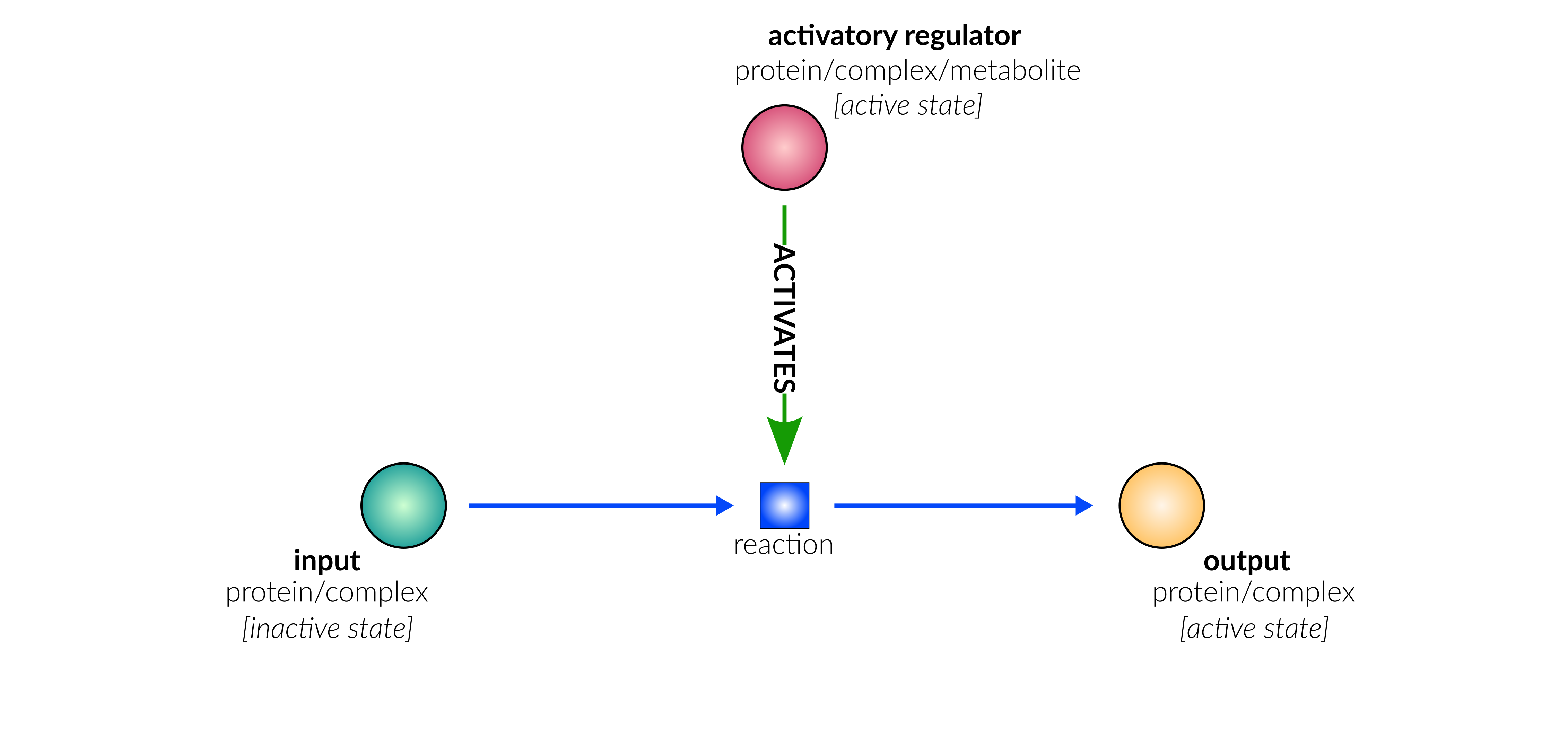
transcriptional/translational activation
Biological representation
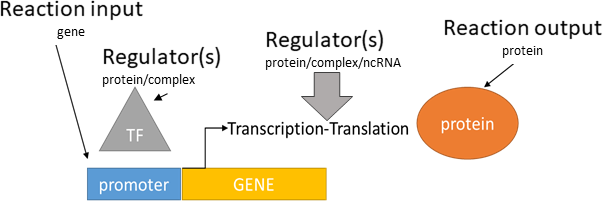
Database representation
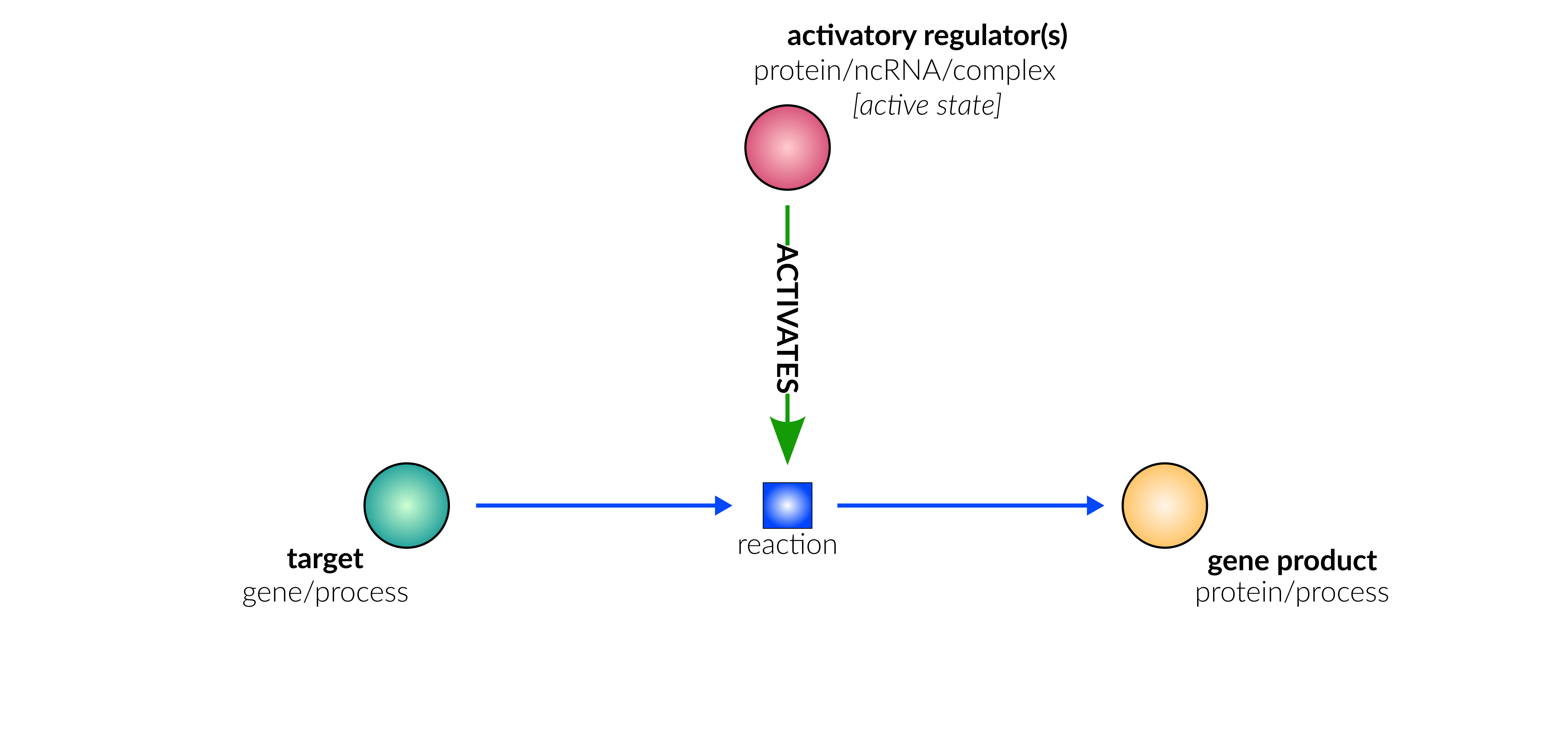
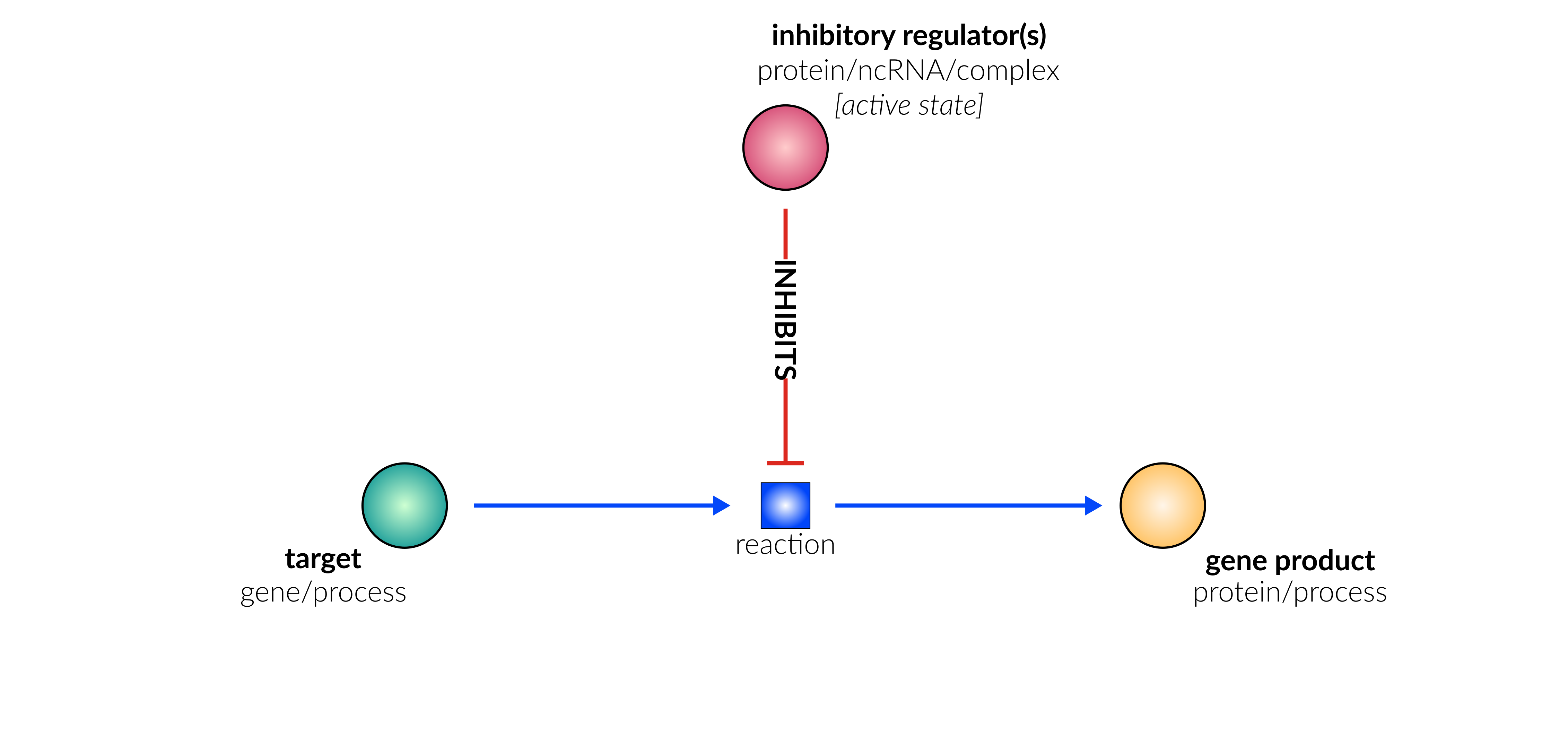
transcriptional/translational repression
Biological representation
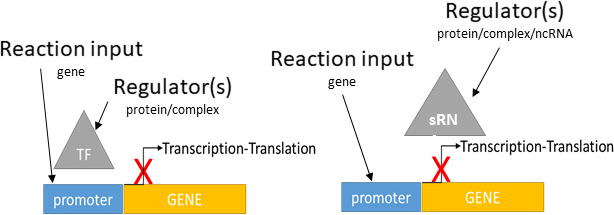
Database representation
translocation
Biological representation
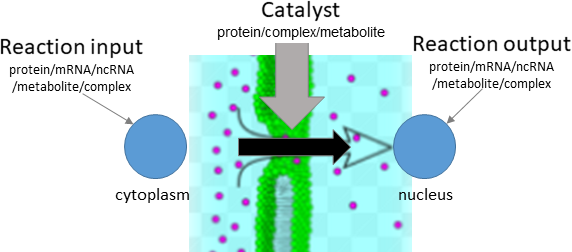
Database representation
unknown
Biological representation
Database representation
Entering the reaction details
A number of metadata fields are provided for the reaction meta data. These are:
- Experimental technique
- (required) The experimental technique(s) that verified the reaction/interaction
- Evidence sentence
- (required) A statement defining the reaction/interaction. Preferably a direct quote from the source.
- Additional information
- (optional) Any pertinent additional information that should be noted. For example, if the reaction occurs only under certain conditions, these should be stated here.
- Organ
- (optional) The plant organ where reaction was observed. (In translocation reaction, where the translocated substrate originated.).
In the next step reaction participants ("nodes") should be entered, these are the inputs/substrates, regulators/catalysts and output/products. Based on the selected reaction type, both the type of participant and the number of participants per field will be limited.
The following node types are available (but not in all reactions):
- metabolite
- mRNA
- miRNA
- ncRNA
- gene
- protein
- abstract
- complex
- process
- (foreign) mRNA
- (foreign) gene
- (foreign) protein
- (foreign) entity
- (foreign) abstract
- (foreign) abiotic
The foreign nodes refer to external actors, such virus, bacteria, etc.
The foreign abiotic entity includes stressors such as heat or drought. When entering a abiotic factor, be as general as possible (e.g. 'heat'), and include details (e.g. the degree or length of the treatment) in "Additional information".
When entering metabolite, complex, abstract, process or foreign nodes, the name is required and used to link to nodes present in the database.
For mRNA, miRNA, ncRNA, gene, and protein entities, the plant identifier is required. A name field is available only for assistance in finding the correct identifier. In some cases, if the identifier is not yet in the database, or is is entered under a different short-name, the identifier needs to be entered into the identifier field manually.
If the plant entity has no standard identifier, or is some unspecified gene, the "abstract" node type should be selected.
Once the reaction details are entered, the "Check" button compiles the reaction information, and returns with issue if there are. Nodes that where not found in the database, will be annotated with an option to add them before proceeding. A summary of the reaction data is also provided to examine for consistency.
Once all errors are cleared, the submit button can be pressed. On successful entry, a reaction id will be returned.
Entering a new component
When a reaction participant was not found in the database, the contributor can enter it. Depending on the type of node, the node input for has a number of fields.
For plant nodes (mRNA, miRNA, ncRNA, gene, and protein entities), the fields are:
- Gene identifier
- (required) The gene identifier (e.g. AT5G38410).
- Gene sequence
- (occasionally required) If the identifier is not able to be validated with GoMapMan, the gene sequence is required.
- Species
- (required) Select the correct species for the gene.
- Short name
- (required) Gene or gene family short name.
- Full name/description
- (optional) A description of the gene, e.g. synonyms, full name, etc.
- Pathway
- (optional) Select the correct pathway that the node takes part in.
- External Links
- (optional) If available, add the ChEBI, PubChen and/or MetaCyc identifiers for the node.
For plant abstract entities, the fields are:
- Species
- (required) Select the correct species for the gene.
- Short name
- (required) Gene or gene family short name.
- Full name/description
- (optional) A description of the gene, e.g. synonyms, full name, etc.
- Pathway
- (optional) Select the correct pathway that the node takes part in.
- External Links
- (optional) If available, add the ChEBI, PubChen and/or MetaCyc identifiers for the node.
For metabolites, the fields are:
- Name
- (required) The name of the metabolite.
- Description
- (optional) A description of the metabolite, e.g. synonyms, full name, etc.
- Pathway
- (optional) Select the correct pathway that the node takes part in.
- External Links
- (optional) If available, add the ChEBI, PubChen and/or MetaCyc identifiers for the node.
For complexes, the fields are:
- Sub-units
- (required) Complex sub-units or components. Use "Add another" to add multiple sub-units.
- Description
- (optional) A description of the complex, e.g. synonyms, full name, etc.
- Pathway
- (optional) Select the correct pathway that the node takes part in.
- External Links
- (optional) If available, add the ChEBI, PubChen and/or MetaCyc identifiers for the node.
When a complex is added, the name is automatically generated from the sub-unit names. Please node the name before returning the the reaction entry page.
For processes, the fields are:
- Name
- (required) The name of the process.
- Description
- (optional) A description of the process, e.g. synonyms, full name, etc.
- Pathway
- (optional) Select the correct pathway that the process takes part in.
- External Links
- (optional) If available, add the ChEBI, PubChen and/or MetaCyc identifiers for the process.
For foreign nodes, the fields are:
- Foreign entity name
- (required) The name of the entity.
- Classification
- (required) Choose the appropriate classification, e.g. bacteria, fungi, ... or other.
- Species
- (required) Input the correct species for the node (in the case of aboitic, this should be a sub-classification, e.g "heat".
- Description
- (optional) A description of the process, e.g. synonyms, full name, etc.
- Pathway
- (optional) Select the correct pathway that the process takes part in.
- External Links
- (optional) If available, add the ChEBI, PubChen and/or MetaCyc identifiers for the entity.
For abiotic nodes, the fields are:
- Abiotic factor name
- (required) The name of the entity.
- Description
- (optional) A description of the factor, e.g. synonyms, full name, etc.
- Pathway
- (optional) Select the correct pathway that the factor takes part in.