PSS neo4j database
Basic schema
The basic schema of the PSS database (in terms of reactions) is shown below:
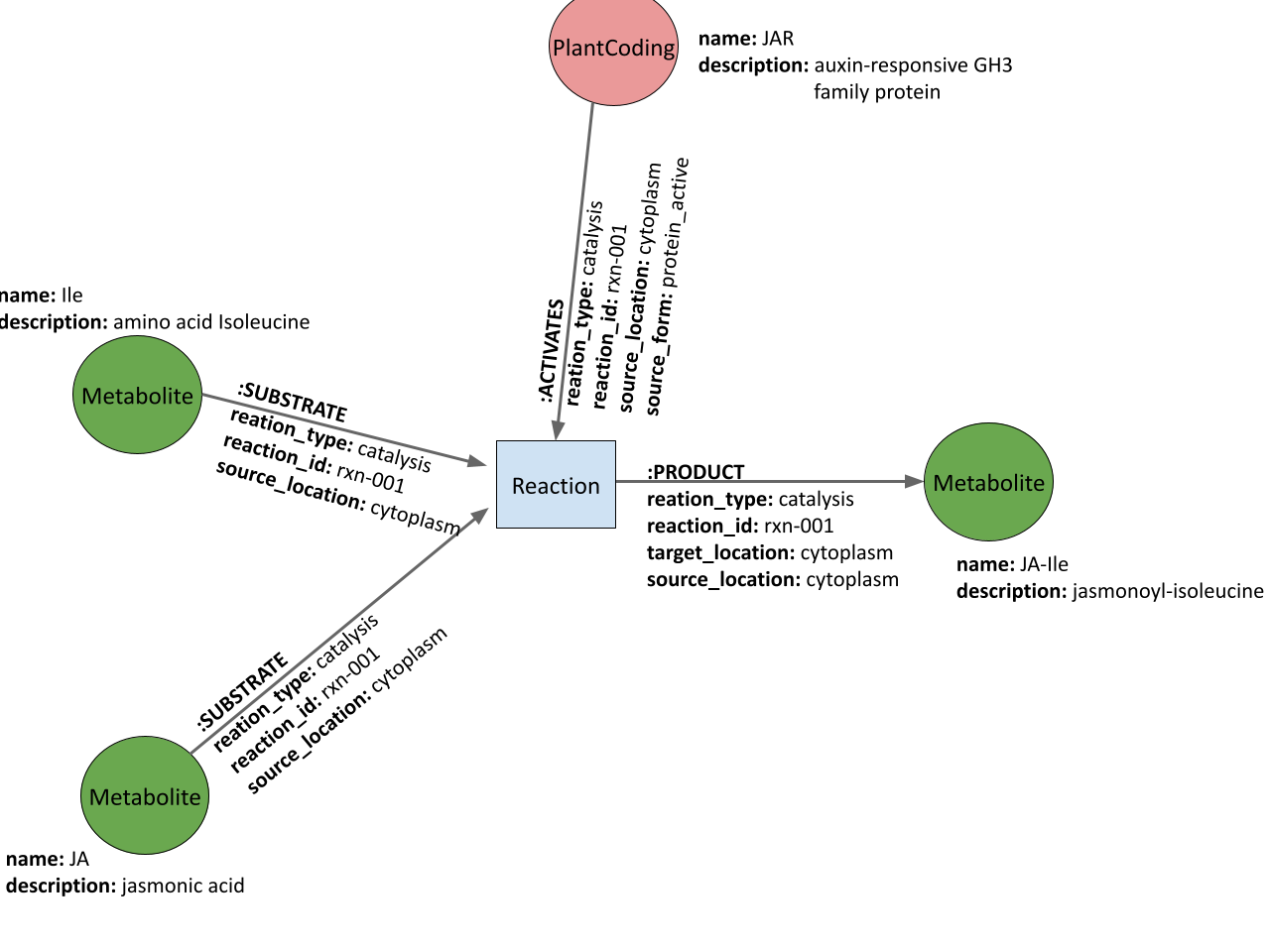
For a more detailed description of the schema, see: PSS database schema
Cypher querying language
The standard query language to interface with a neo4j database is Cypher. In Cypher nodes are represented by () and relationships are represented by -[]->. An edge therefore has the following general syntax:
(source)-[relationship]->(target)
| The following patterns apply to nodes: | |
|---|---|
| () | any node, no assigned variable |
| (:Metabolite) | any Metabolite node |
| (m:Metabolite) | any Metabolite node, assigned to variable m |
| ( {<property>:<value>}) | any node with property equal to value |
| The following patterns apply to relationships: | |
| ()--() | any relationship |
| ()-[:SUBSTRATE]-() | any substrate relationship |
| ()-[{<property>:<value>}]-() | any relationship with property equal to value |
| ()-[p:SUBSTRATE]-() | any substrate relationship and assign to a variable called p |
| (:Metabolite)-[:SUBSTRATE]-(:Reaction) | any substrate relationship between a Metabolite and a Reaction |
| (:Metabolite)-[:SUBSTRATE]->(:Reaction) | any substrate relationship with Metabolite source and Reaction target (i.e. directed) |
| Basic query structures: | |
| MATCH <pattern> | searches for the given pattern in the db (SELECT in SQL) |
| OPTIONAL MATCH | searches for the given pattern in the db, results in NULL if no match (still returns) |
| WHERE | filter result, can be combined with AND OR XOR NOT |
| WHERE <entity.property> <comparison> <value> | Comparisons include:
=< > <= >= =~ (a regex expression) IN (a list) |
| WHERE | More filter options: exists(<pattern>) <entity.property> STARTS WITH <entity.property> ENDS WITH <entity.property> CONTAINS |
| RETURN <result> | returns values or results of a query |
| RETURN <result> AS <alias> | return result with an alias property key instead of property name |
| DISTINCT | filters to unique set |
Further statements:
- CREATE
- SET
- MERGE
- DELETE
- REMOVE
See also result aggregation etc.
Here are two sources for further reading:
Example cypher statements
- Fetch all nodes:
-
MATCH (n)
RETURN DISTINCT n.name AS name - Fetch all undirected neighbours of JAR:
-
MATCH (n {name:"JAR"})--()
RETURN DISTINCT other.name AS name
Installation and deployment by Docker
-
Installation
First, install Docker on your computer. The instructions can be found at: Get Docker.
-
Clone the repository
Clone the repository to your computer:
git clone https://github.com/nib-si/skm-neo4j.gitThe correct branch is ---:
cd skm-neo4j git checkout ---The repository is organised as follows:
skm-neo4j ├─ docker-compose.yaml ├─ docker-entrypoint.sh ├─ dockerfile ├─ conf ├─ logs ├─ data . ├─ dumps . ├─ raw . ├─ import . └─ db ├─ work └─ docs └─readme.md
docker-compose file
neo4j startup script
neo4j container build script
contains configuration files for neo4j and plugins
for neo4j logging
contains dumped databases
raw, original data (dev only)
for neo4j importing (dev only)
neo4j graph storage volume (dev only)
work scripts & notebooks
documentation folder -
Set up neo4j database
to deploy the graph database on your computer as a container, you will need docker installed.
in the repository root folder, build the neo4j container with the graph:
cd skm-neo4j docker build --tag skm-graph .To run this image:
docker run -it \ -p7474:7474 -p1337:1337 -p7687:7687 \ -v$pwd/logs:/logs -v$pwd/conf:/conf skm-graphAnd visit the neo4j browser at http://localhost:7474/.
Link the neo4j database to a Jupyter notebook
Start up the neo4j database and link a jupyter notebook using docker-compose. To run the first time, navigate to the repo folder (containing docker-compose.yml) and run:
docker-compose upThereafter you can use:
docker-compose startOpen your browser at the http://localhost:8888/?token=... link printed to the terminal. If the logs are not printed, run
docker-compose logs | grep 'http://localhost:.*/?token' | tail -1to find the correct link.
To stop the containers, use:
docker-compose stopOr to stop and remove them:
docker-compose down -
Remove database
If you need to remove the graph image, first remove the container:
docker-compose downOr get the container ID from the first column in:
docker ps -a | grep skm-graphAnd delete it using:
docker rm <container id>Then delete the image:
docker rmi skm-graphDelete the folder with the graph data (if it exists).
sudo rm -rf data/db/* -
Dump a neo4j graph from Docker
In neo4j enterprise edition, follow instructions here.
For community edition, do the following
-
Start up a neo4j container, without starting the neo4j database:
docker run \ --volume=$pwd/data/db/:/data \ --volume=$pwd/data/dumps:/dumps \ --ulimit=nofile=40000:40000 \ --user=1000:1000 \ -it \ neo4j:4.3.2 \ /bin/bash
-
In the container, use neo4j-admin to dump the graph:
bin/neo4j-admin dump --database=skm --to=/dumps/skm.dump
Ctrl + d to exit the container.
-
Remove the new container:
docker rm dump
-