Welcome to Stress Knowledge Map!
SKM is a compilation of knowledge on mechanisms underlying responses of plants to stress, the so called stress signalling network. Of course, responses to stress are tightly connected to growth and developmental signalling, so in some parts these processes are also included to provide a complete picture.
Knowledge was compiled by manual inspection of manuscripts, knowledge provided in several knowledge databases and from datasets published as supplemental materials. Only information on direct physical interaction is included:
- Protein - protein interactions
- Protein - DNA interactions, e.g. transcriptional regulation
- smallRNA - transcript interactions
- Enzymatic transformations of metabolites
The signalling network is composed of nodes and connections. Connections are of different types, in line with above listed physical interaction types. Nodes represent different molecular entities:
- genes/transcripts/proteins/active proteins
- smallRNAs
- metabolites
Stress Knowledge Map is currently focusing on the following species: Arabidopsis thaliana, potato, tomato, and poplar, thus only experiments performed on those species are included.
Two knowledge graphs are available in Stress Knowledge Map:
PSS
The mechanistic Plant Stress Signalling model
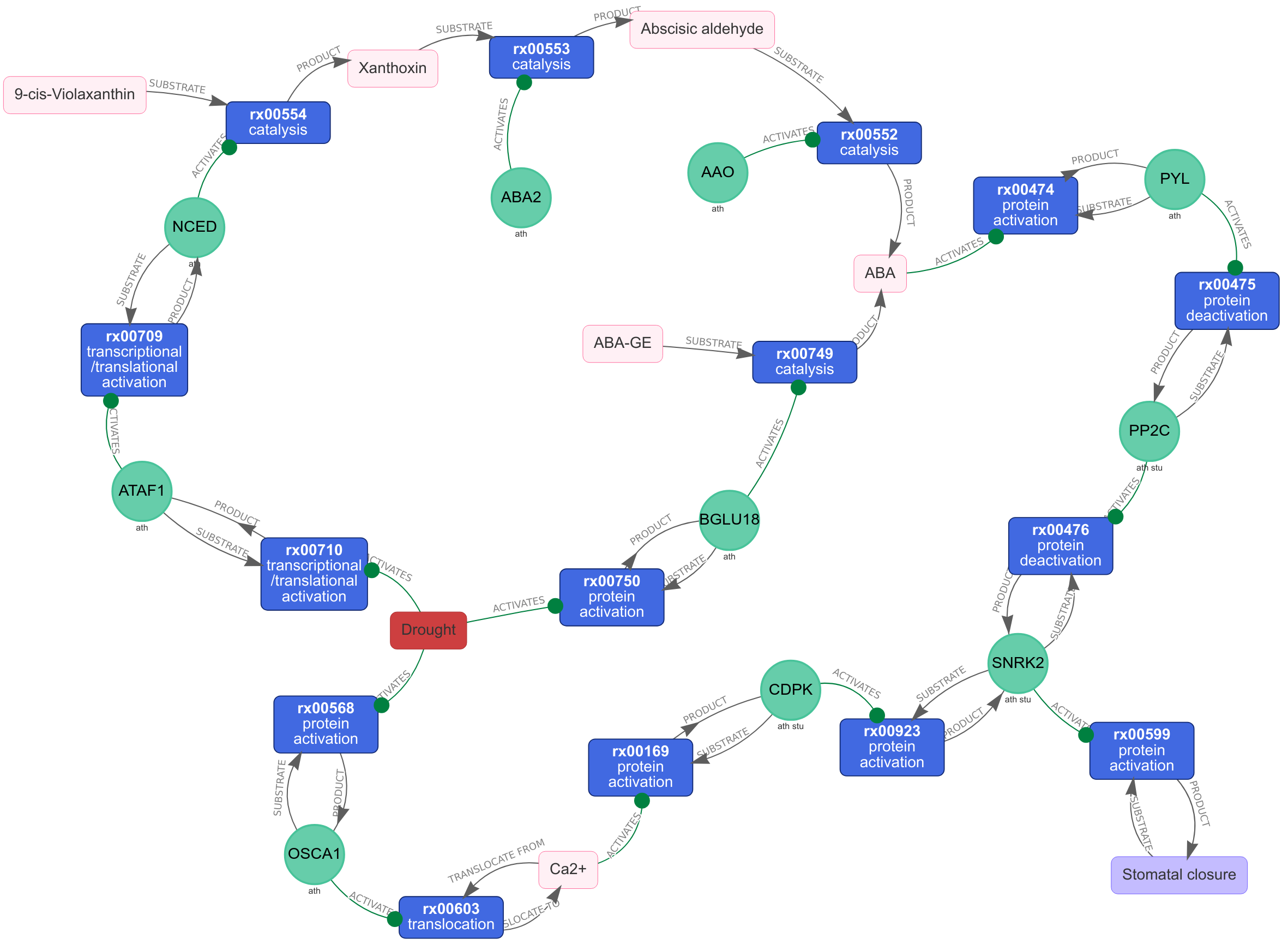
PSS is an ongoing endeavour to assemble an accurate and detailed mechanistic model of plant stress signalling by extracting validated molecular interactions from published resources. PSS includes the complete stress response cascade within the plant cell, initiating with abiotic and biotic stressors. Stress perception through receptors initiates Ca2+, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and MAPK signalling cascades, as well as phytohormone biosynthesis and signaling pathways, including abscisic acid (ABA), jasmonic acid (JA), salicylic acid (SA), ethylene (ET), auxin (IAA), gibberellins (GA), and cytokinins (CK). These translate perception into a cellular response, resulting in the activation of processes that execute protection against stress. Relevant transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation, and intersections with growth and development are also included.
Entities in PSS include genes and gene products, complexes, metabolites, and triggers of plant stress. Interactions between these entities include protein–DNA (e.g., transcriptional regulation), non-coding RNA–transcript, and protein–protein interactions, as well as enzymatic catalysis and transport reactions.
The majority of interactions in PSS have been compiled from peer-reviewed articles with targeted experimental methodology, which normally means that the results are confirmed by at least two independent approaches. PSS also contains relevant pathways from KEGG and AraCyc.
The formalism of knowledge in PSS allows for different types of data integration and mechanistic modelling, from boolean to ODE and more.
Explore PSS with the interactive search and visualisation tool:
PSS Explorer
(or click on the image above to see a drought induced network)
CKN
The Comprehensive Knowledge Network
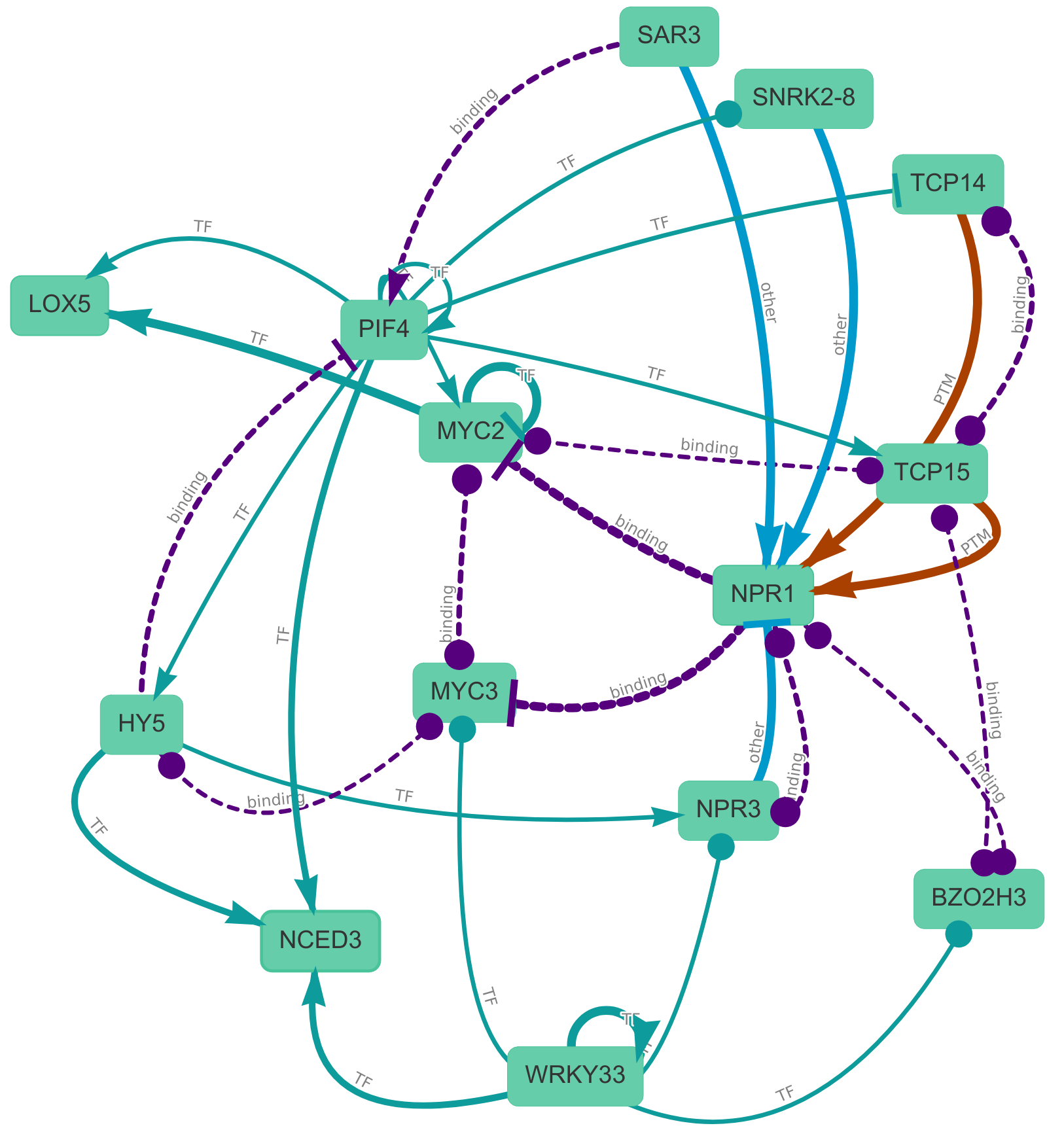
CKN is a large-scale condition-agnostic assembly of current knowledge on experimentally observed physical interactions between molecular interactions in Arabidopsis thaliana, offering broader insights into not only stress signalling but also any other plant process. These interactions encompassing protein–DNA interactions, interactions of non-coding RNA with transcripts, post-translational modifications, and protein–protein interactions.
CKN contains 26, 234 entities (24, 829 of which are genes in Araport) and almost half a million interactions. CKN includes all relevant reactions from PSS v1.0, but also information that is slightly less reliable than in PSS, (for example high throughput experiments such as ChIp-Seq and DAP-Seq, and large scale PPI experiments). Some predicted interactions are also included, but never interactions inferred from co-expression analysis or similar. A ranking system for the interaction reliability (based on experimental approach) enables researchers to evaluate the biological credibility and relevance of individual interactions.
Knowledge in CKN is network based, thus it can be used for data contextualisation and hypothesis generation, but is not compatible with all types of modelling.
Explore CKN with the interactive search and visualisation tool:
CKN Explorer
(or click on the image above to see a LOX-NCED-NPR induced network)
Further use of SKM
Aside from PSS Explorer and CKN Explorer, both knowledge graphs are available for download for analysis or modelling.
For inspiration, take a look at the analysis options provided in our Python toolkit on GitHub: github.com/NIB-SI/skm-tools.
Enter a interaction that is still missing in mechanistic Plant Stress Signalling model: Contribute (note that contributions require an account).
If you have used Stress Knowledge Map in your research please cite:
Latest Updates
Exploring Ca²⁺ and H₂O₂ Crosstalk in Barley with the Stress Knowledge Map
by Carissa on 2025-04-09
We are pleased to highlight a recent collaborative study that utilized the Stress Knowledge Map (SKM) to investigate the interplay between calcium and redox signalling in barley. The research, titled "Ca²⁺-dependent H₂O₂ response in roots and leaves of barley—a transcriptomic investigation," was ... Read more
Training Workshop for Stress Knowledge Map
by Carissa on 2024-06-18
Thank you to all that attended our workshop! The slides are available here: Slides We ... Read more
Celebrating the publication of Stress Knowledge Map in Plant Communications
by Carissa on 2024-06-14
We are thrilled to announce the publication of our article in Plant Communications titled "Stress Knowledge Map: A Knowledge Graph Resource for Systems Biology Analysis of Plant Stress Responses." This comprehensive resource, developed by an international team of experts led by dr. Kristin ... Read more